While medical insurance is acquired primarily for its protective function, the intricacies of the claims process are frequently overlooked, leading to confusion and frustration when claims are denied. This article offers a comprehensive examination of each stage of the claims process, addresses common challenges, and provides a thorough overview of medical insurance.
Be Prepared by Understanding the 3 Steps to Making Claims
1. Prepare Relevant Documents and Lodge the Claim by the Deadline
The first step in the claims process is for the policyholder to submit the claim form and supporting documents by the specified date. The documents usually include:
- A claim form (sometimes completed by the attending doctor and stamped by the hospital)
- Original copies of medical receipts and invoices
- Copies of diagnostic or laboratory reports
- Referral letters from the doctor or hospital
- Copies of the Hong Kong Identity Card for both the policyholder and the insured
2. Complete the Claim Form, Submit the Application, and Wait for Approval
Complete the claim form provided by the insurer and submit it using one of the available methods. Applications could be submitted in person, by post, by email orthrough mobile apps for added convenience.
After submission, simply wait for the approval. The approval period can vary depending on the case type. Insurance companies handle cases promptly, and the insured can inquire about the progress if needed.
3. Get Your Claims
Once your application is approved, the insured amount will be deposited into your designated bank account on the specified working day.
Is the Process Even Simpler If Cashless Medical Service is Included?
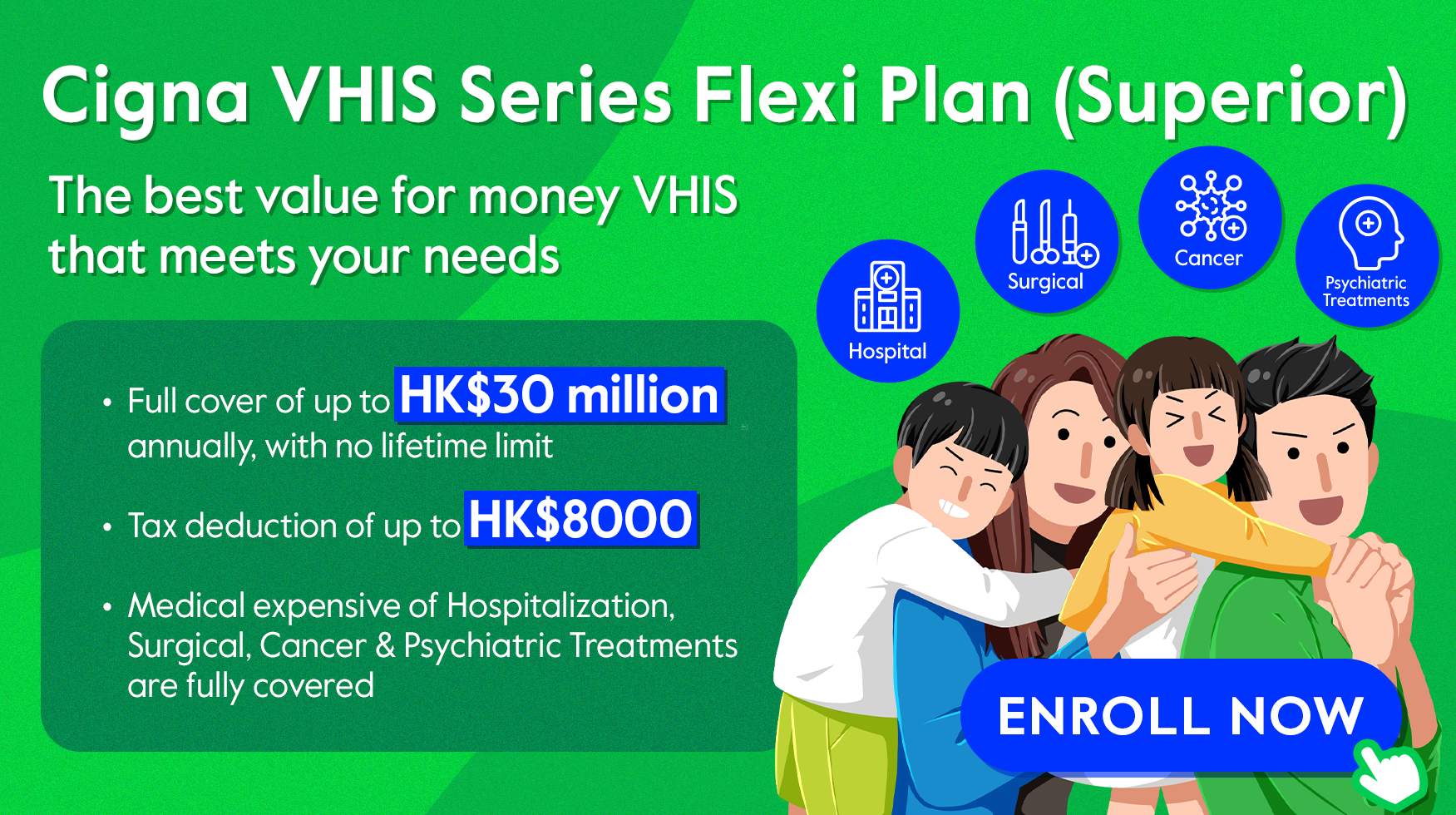
Many medical plans today offer Cashless Medical Service, which enhance the claims process and provide extra convenience for the insured. For example, with the Cigna VHIS Series, a client can submit an application before hospital admission. Once approved, the insurer will directly pay the pre-authorized amount to the medical service provider. This allows you to focus on regaining your health without worrying about unexpected medical expenses.
How to Avoid Claim Denials?
Claim denials and partial payouts are common disputes between policyholders and insurance companies. These situations are often attributed to the following reasons:
1. Non-Disclosure of Material Facts
Insurance contracts are based on the principle of “utmost good faith.” Policyholders must proactively disclose their health condition and medical history to allow the insurer to assess the risks. Failure to disclose complete medical history may result in policy invalidation or claim denial. To ensure adequate coverage, clients should complete the insurance application form accurately and disclose all requested information. Any changes in health condition after purchasing an insurance policy should also be reported to the insurer.
2. Involving “Exclusions”
Insurance policies typically contain exclusions, which are specific medical conditions or treatments that are not covered. Common exclusions include pre-existing conditions. Additionally, some plans may not cover day surgery or outpatient procedures. It is essential to carefully review your policy to understand both its coverage and exclusions.
3. Falling Short of “Medically Necessary” and “Reasonable and Customary” Standards
“Medically necessary” and “reasonable and customary” criteria are outlined in the insurance policy clauses. To avoid disputes, make sure the medical procedures received by the insured are necessary for diagnosis or treatment purposes. Verify with the insurer before undergoing non-emergency hospitalisations, and evaluate the costs provided by the doctor. One of the examples is the “reason for hospitalization”. Many surgical procedures or treatments can now be performed in clinics at a lower cost than in hospitals. The insurer may question the necessity of hospitalizing a patient for certain procedures.
On the other hand, “Reasonable and Customary” charges are determined by comparing the costs of similar procedures across various private hospitals, medical institutions, and surgeons, as well as by analyzing claims data and the Hospital Authority’s private services. If the actual charges exceed these benchmarks, the insurer may only cover a portion of the costs. Therefore, the insured should understand their policy’s coverage and exclusions and disclose their medical history in detail to increase their chances of a successful claim.
Source
© Cigna Healthcare 2023
Information provided in this article is intended for health and fitness purposes only and is not intended for use in the diagnosis of disease or other conditions, or in the cure, mitigation, treatment or prevention of disease (see Terms & Conditions for details). Any health-related information found in this article is available only for your interest and should not be treated as medical advice. Users should seek any medical advice from a physician, especially before self-diagnosing any ailment or embarking on any new lifestyle or exercise regime. Any information contained in this article may not be suitable, accurate, complete or reliable. Cigna Healthcare accepts no responsibility for the content or accuracy of information contained on external websites or resources, or for the security and safety of using them. "Cigna Healthcare" and the "Tree of Life" logo are registered trademarks of Cigna Intellectual Property, Inc. in the United States and elsewhere, licensed for use. All products and services are provided by or through operating subsidiaries, and not by The Cigna Group.