Do you experience prolonged abdominal pain with symptoms such as fever, chills, and vomiting? If so, you may have gallbladder stones (or gallstones). Without proper treatments, gallstones can even lead to sepsis. In this article, Cigna Smart Health explains what gallstones are with their causes, symptoms and treatments.
What are Gallbladder Stones?
Gallstones are pieces of solid material that form in your gallbladder, and they are one of the common digestive conditions. Your gallbladder stores and releases bile, a fluid made in your liver, to help digestion. Bile also carries wastes like cholesteroland bilirubin. These materials can be hardened and form gallstones. Typically, there are two types:
1. Cholesterol stones
They are the most common type of gallbladder stones, accounting for about 80% of all cases. Yellow-green crystals are formed due to excessive cholesterol.
2. Pigment stones
Made of bilirubin, the gallstones are smaller with darker brown or black.
Causes of Gallbladder Stones
According to the statistics, the incidence among adults is around 10%. In other words, 1 in 10 adults gets gallstones. It is common among individuals aged 40 to 50. However, the exact causes of gallbladder stones are still unclear, but the below factors may raise the risk of gallstones.
- Overweight or obese; eating a high-fat or high-cholesterol diet
- Having an irregular diet
- Being female (who have a higher risk than male)
- Being age 40 or older
- Having a family history of gallstones
- Having other diseases (such as diabetes, sickle cell anemia, lung diseases etc.)
Symptoms of Gallbladder Stones
Generally, gallstones may cause no signs or symptoms at first. If you observe the following symptoms persistently, please pay more attention and seek medical advice at your earliest advance.
- Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the centre or upper right portion of your abdomen, just below your breastbone
- Pain in your right shoulder
- Nausea or vomiting
- Jaundice (a yellow tint to the skin and eyes)
- Fever or chills
- Tea-colored urine or stool
How Are Gallbladder Stones Diagnosed?
If you have the above symptoms prolonged and are suspected, your doctor may conduct the below tests to detect gallstones.
1. Ultrasound
An ultrasound produces images of your abdomen and shows the location(s) of the gallstones.
2. Imaging with iodine
An iodine pill or an injection of special iodine dye is given to make the biliary system and gallstone location appear on X-ray images.
3. ERCP (Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography)
A long, flexible telescope at the end is guided through the mouth and down through the stomach into the small intestine. This enables your doctor to view the ducts directly and locate any stones.
4. Blood and urine tests
The tests may reveal infection, jaundice, pancreatitis or other complications caused by gallstones.
Treatments of Gallbladder Stones
The most common treatment for gallstones is to remove the gallbladder surgically. This surgery can be performed laparoscopically, a minimally invasive technique with less post-operative pain and a faster recovery than conventional cholecystectomy. However, your doctor may opt for conventional cholecystectomy to resect your gallbladder due to severe inflammation or other notable conditions. Below are the three common gallstones treatments.
1. Medications to dissolve gallstones
For those with smaller gallstones, your doctor may use medications to break up the stones, such as ursodeoxycholic acid, for discharging out of the body. However, the treatment’s effectiveness is limited, depending on the composition and size of gallstones, as well as the absorption of the medicine by the gallbladder.
2. Cholecystectomy
If laparoscopic surgery is not possible, conventional cholecystectomy is required. Your doctor needs to make a big cut (around 10cm) in your belly to remove gallstones, release the bile out of your body and eventually resect the gall bladder. Open cholecystectomy. You have to stay in the hospital for a week afterward for wound healing.
3. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
This is the most common treatment. After a general anaesthetic, several tiny cuts (usually four) are made in the abdomen, through which surgical instruments and a miniature video camera are inserted. The gallbladder is removed without cutting through any abdominal muscles, and if necessary, ERCP (see above) can be used to locate and remove stones in the bile duct. This surgery causes less pain and fewer complications than surgery involving larger cuts in the abdomen.
Complications of Gallbladder Stones
Untreated gallstones and delayed treatments may result in bacterial infection in blood, cholecystitis, cholangitis, pancreatitis and other life-threatening complications, including:
1. Acute cholecystitis
A gallstone that becomes lodged in the neck of the gallbladder can cause inflammation due to the accumulation of bile. Cholecystitis can cause severe pain, fever and even death.
2. Blockage of the common bile duct
Gallstones can block the ducts through which bile flows from your gallbladder or liver to your small intestine. Severe pain, jaundice, bile duct infection, pancreatitis and sickle cell anemia can result.
3. Gallbladder cancer
People with a history of gallstones have an increased risk of gallbladder cancer since the stones can lead to mutations at the gallbladder membrane, contributing to cancer.
Eating And Diet for Gallbladder Stones
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases suggests that gallstone patients have a healthy diet and average weight. Below are some tips given by the authority.
- Intake of unsaturated fatty acids (such as nuts, olive oil, avocado)
- Eat foods rich in dietary fibre (such as vegetables, fruits, beans, brown rice, oats)
- Avoid unhealthy sauces or oils in desserts and deep-fried dishes
- Avoid extremely low-calorie diets
Preventing Gallbladder Stones
Although there is no definite ways of prevention for gallstones, you can reduce your risk if you can follow the below tips.
- Exercise regularly
- Control your cholesterol level
- Maintain a normal weight
- Reduce your intake of saturated fatty acids
- Avoid having refined carbohydrates
Apart from lifestyle and dietary changes, you should have a thorough examination of your body at the hospital to lower the incidence of gallstones, receive proper treatments in time and mitigate its adverse effect bringing to your health.
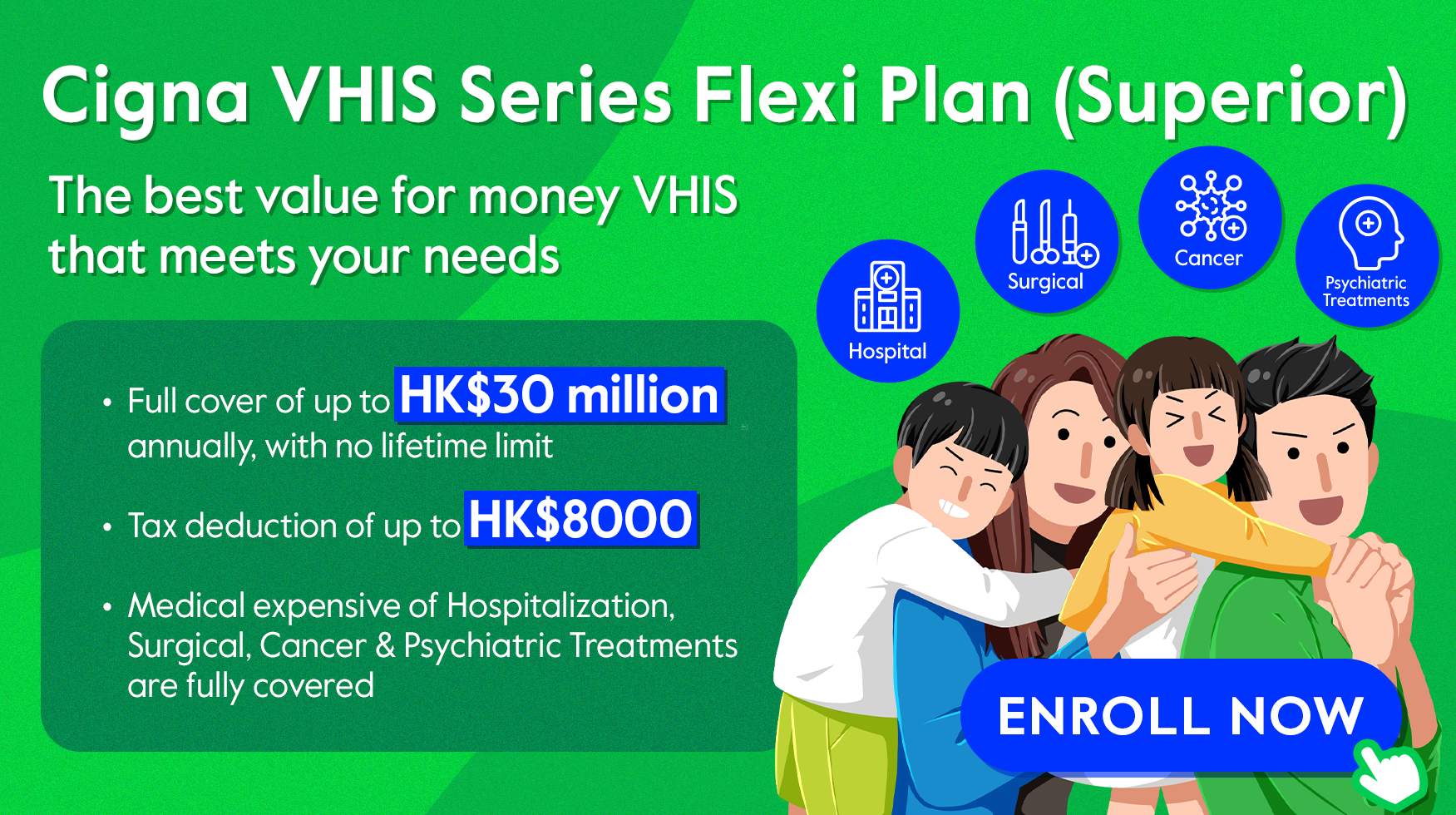
1 in 10 adults has gallbladder stones. Regular check-ups can discover hidden health issues in advance. Cigna VHIS Flexi Plan (Superior) offers coverage of up to HK$30,000,000 with no lifetime limit, and medical expenses are fully covered. No need to worry about future medical expenses! The plan also covers for unknown pre-existing conditions, congenital conditions, non-surgical cancer treatment, day-case procedures and advanced diagnostic imaging tests etc., ensuring your medical needs are met. Click here to learn more!
Source
© Cigna Healthcare 2023
Information provided in this article is intended for health and fitness purposes only and is not intended for use in the diagnosis of disease or other conditions, or in the cure, mitigation, treatment or prevention of disease (see Terms & Conditions for details). Any health-related information found in this article is available only for your interest and should not be treated as medical advice. Users should seek any medical advice from a physician, especially before self-diagnosing any ailment or embarking on any new lifestyle or exercise regime. Any information contained in this article may not be suitable, accurate, complete or reliable. Cigna Healthcare accepts no responsibility for the content or accuracy of information contained on external websites or resources, or for the security and safety of using them. "Cigna Healthcare" and the "Tree of Life" logo are registered trademarks of Cigna Intellectual Property, Inc. in the United States and elsewhere, licensed for use. All products and services are provided by or through operating subsidiaries, and not by The Cigna Group.