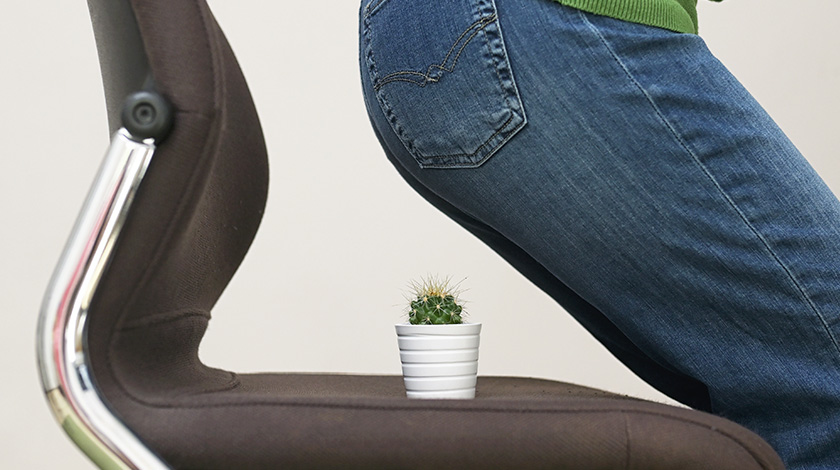
Haemorrhoids are annoying and sometimes embarrassing. They are prevalent that one in three people in the world suffering from them. In Hong Kong, half the people aged over 50 years old have haemorrhoids, and there were 26077 people hospitalised due to haemorrhoids. Haemorrhoids are a common disease in both men and women. For females, haemorrhoids frequently develop during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester and during and shortly after childbirth.
What Are Haemorrhoids?
Also known as piles or cystitis, haemorrhoids are cushions of tissue and varicose veins located in and around the rectal area. In their normal state, they are cushions that help with stool control. When they become inflamed, hypertrophied, loose or burst, the elasticity of the anus decreases, leading to prolapse and haemorrhoids.
The Difference Between Internal And External Hemorrhoids
The dentate line at the anal canal is considered as the division of internal and external haemorrhoids. The positions and symptoms caused by the piles reflect whether they belong to internal or external haemorrhoids.
Internal haemorrhoids lie inside the rectum, and the symptoms include:
- Painless bleeding during defecation
- Itching in your anal region
- Pain in the anus when haemorrhoids are pressured
- Prolapse (rectal prolapse)
External haemorrhoids are under the skin around the anus, and the symptoms include:
- Bleeding at the anus
- Pain at the anus; discomfort when sitting, walking and defecating
- Increased secretions from anal tissues with a peculiar smell
If the piles grow across the dentate line, the haemorrhoids are considered as mixed haemorrhoids.
Four Grades of Haemorrhoids
Although haemorrhoids start inside the anal canal, they prolapse out of the anus for severe cases. A doctor may assign a grade to a prolapsed haemorrhoid based on how far it sticks out.
| Grades |
Features |
| Grade One |
Haemorrhoids locate in the anus without pain and prolapsing. Symptoms include bleeding, increased secretion and feeling itchy. |
| Grade Two |
Prolapsed but will retract by themselves. These may only prolapse when you put pressure on your anal or rectal area, such as straining when you have a bowel movement and then returning to their normal position afterwards. Rectal bleeding is observed. |
| Grade Three |
Prolapsed, and you have to push it back in yourself. These may need to be treated so that they don’t become too painful or infected. |
| Grade Four |
Prolapsed, and you can’t push it back in without a lot of pain. These will usually need to be treated to prevent pain, discomfort, or further complications. |
What Causes Haemorrhoids?
The causes of haemorrhoids are numerous, but most of them are related to lifestyle habits. Eating healthy and staying active can indeed prevent haemorrhoids.
Bowel habits
- Sitting for long periods on the toilet, especially those reading and using their mobiles
- Persistent constipation and straining
Eating habits
- Having a low-fibre diet
- Eating spicy foods usually
Living habits
- Lack of exercises leads to poor digestion
- Sitting or standing for long periods pressures the rectum
Other uncontrollable factors
- Family history
- Pregnancy
- Obesity
- Ageing
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids
For severe cases, your doctor may suggest medication or surgeries.
Medications here mostly refer to topical treatments, including an over-the-counter haemorrhoid cream and suppository containing hydrocortisone. To relieve the discomfort caused by mild haemorrhoids, you should also eat more high-fibre foods, drink more liquid (mostly water) and have a regular bowel movement.
Treatment options of haemorrhoids include:
| Treatments |
Procedure |
Grades |
Duration |
Recovery Time |
Advantages |
| Hemorrhoidectomy |
Traditional open surgery that can resect internal and external haemorrhoids |
1-4 |
~1 hour |
A few days after the surgery |
Low recurrence rate; more thorough resection |
| Rubber band ligation |
One or two tiny rubber bands are placed around the base of an internal hemorrhoid to cut off its circulation. The haemorrhoid withers and falls off within a week. |
1,2 |
~15 mins |
Shorter-term |
Resection and hospitalisation are not required; mild pain |
| Ultroid Hemorrhoid Treatment |
It uses an electrical current (“direct current”) to create a chemical reaction in the hemorrhoidal tissue, causing the haemorrhoid to scar and shrink within 7 to 10 days. |
1,2 |
~30 mins |
Shorter-term |
Hospitalisation is not required; simple postoperative care |
| Haemorrhoid stapling |
The procedure removes abnormally enlarged hemorrhoidal tissue, followed by repositioning the remaining hemorrhoidal tissue back to its normal anatomic position (3-5cm inside the anus). The haemorrhoid withers and falls off. |
2-4 |
~30 mins |
1-2 days after the surgery |
Hospitalisation is not required; quick recovery and mild pain |
| Infrared photocoagulation |
Within a second, the procedure creates an intense beam of infrared light that causes scar tissues and cuts off the haemorrhoid’s blood supply. |
1,2 |
~10 mins |
Shorter-term |
Hospitalisation is not required; quick recovery and mild pain |
Sources: Hong Kong Haemorrhoid Centre, HMC Hemorrhoid Centre
Fees of Hemorrhoidectomy at Private Hospitals
Below are the charges of hemorrhoidectomy for your reference.
1. Day surgery
| Hospitals / Medical Centres |
Items |
Fees (HKD)* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Inpatient surgery
| Hospitals |
Items |
Package Fees (HKD)* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*Prices as of 11 Feb 2021
Note: Some of the plans do not include special procedures. For detailed pricing, please contact the respective hospital.
5 Prevention Tips for Hemorrhoid
As with any disease, prevention is better than cure for haemorrhoids. Below are some tips to lower your chance of having haemorrhoids.
- Eat enough fibre-rich foods every day to prevent constipation. Every adult should take in more than 25g of dietary fibre. Here are some references, such as an apple (4.4g of fibre), a half bowl of cooked red beans (8.8g of fibres). You should have 2 servings of fruits with 3 servings of vegetables daily.
- Develop a regular bowel habit.
- Don’t strain when trying to pass a stool.
- Every adult should do at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activities, such as cycling, social dancing and pacing, for preventing constipation and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Avoid long periods of sitting and standing at work and spare time: Try to stand, take a walk or break for 5 minutes every hour.
Cigna HealthFirst Elite 360 Medical Plan offers comprehensive and personalized medical coverage across the stage prevention, diagnosis, treatment and recovery, with a range of hospital and surgical benefits, optional insurance benefits with an annual limit of up to HK$50 million, personalized health assessment, three critical illnesses(cancer, stroke and heart attack) all-rounded care and international medical concierge service. A 360-degree total health protection that spans across all the key stages of your health journey. Learn more here.
Sources:
© Cigna Healthcare 2023
Information provided in this article is intended for health and fitness purposes only and is not intended for use in the diagnosis of disease or other conditions, or in the cure, mitigation, treatment or prevention of disease (see Terms & Conditions for details). Any health-related information found in this article is available only for your interest and should not be treated as medical advice. Users should seek any medical advice from a physician, especially before self-diagnosing any ailment or embarking on any new lifestyle or exercise regime. Any information contained in this article may not be suitable, accurate, complete or reliable. Cigna Healthcare accepts no responsibility for the content or accuracy of information contained on external websites or resources, or for the security and safety of using them. "Cigna Healthcare" and the "Tree of Life" logo are registered trademarks of Cigna Intellectual Property, Inc. in the United States and elsewhere, licensed for use. All products and services are provided by or through operating subsidiaries, and not by The Cigna Group.